M Ganesh Kumar
@mgkumar138.bsky.social
210 followers
200 following
33 posts
Computational Neuroscience, Reinforcement Learning. Postdoctoral Fellow @ Harvard. Previously @ A*STAR & NUS. 🇸🇬
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
M Ganesh Kumar
@mgkumar138.bsky.social
· Aug 27
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Ann Kennedy
@antihebbiann.bsky.social
· Aug 20
Theoretical neuroscience has room to grow
Nature Reviews Neuroscience - The goal of theoretical neuroscience is to uncover principles of neural computation through careful design and interpretation of mathematical models. Here, I examine...
www.nature.com
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
M Ganesh Kumar
@mgkumar138.bsky.social
· Aug 19
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
David G. Clark
@david-g-clark.bsky.social
· Aug 19

Connectivity structure and dynamics of nonlinear recurrent neural networks
Studies of the dynamics of nonlinear recurrent neural networks often assume independent and identically distributed couplings, but large-scale connectomics data indicate that biological neural circuit...
arxiv.org
M Ganesh Kumar
@mgkumar138.bsky.social
· Aug 13
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Hyunwoo Gu
@hyunwoogu.bsky.social
· Jul 29
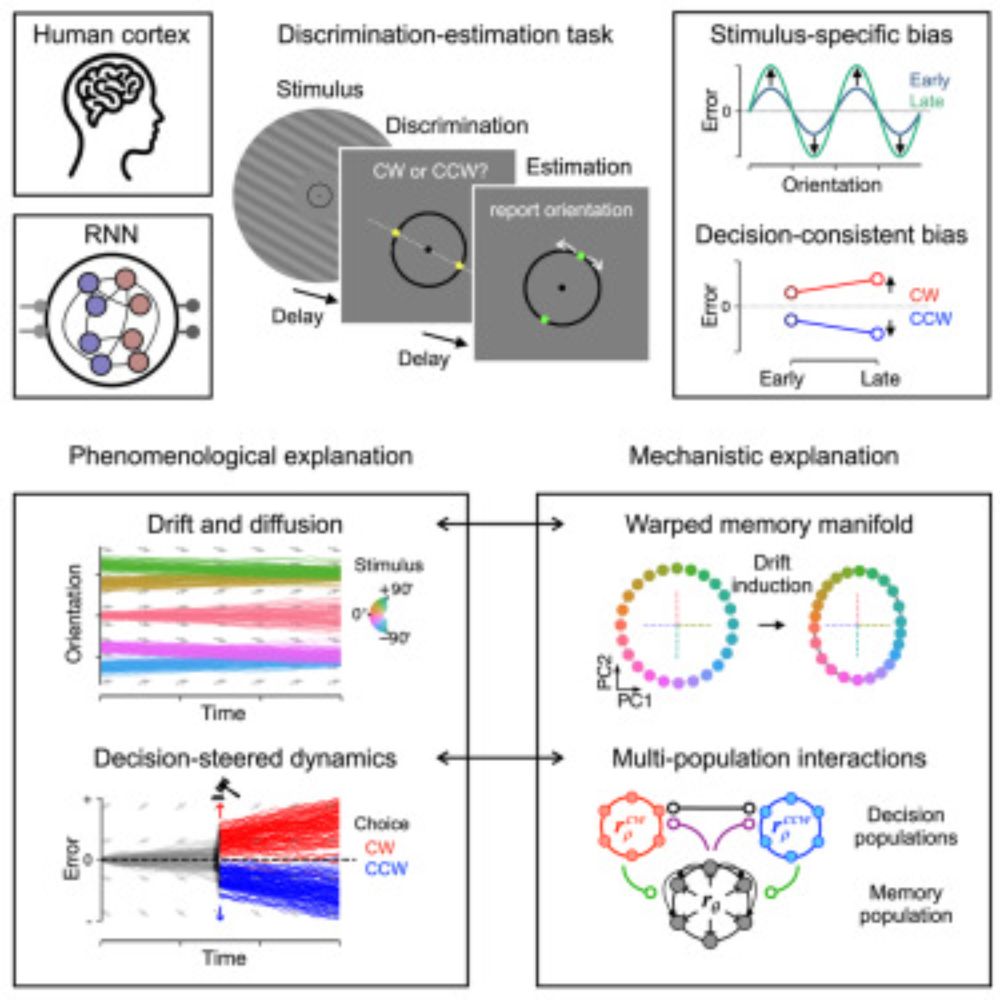
Attractor dynamics of working memory explain a concurrent evolution of stimulus-specific and decision-consistent biases in visual estimation
People exhibit biases when perceiving features of the world, shaped by both external
stimuli and prior decisions. By tracking behavioral, neural, and mechanistic markers
of stimulus- and decision-rela...
dlvr.it
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Sam Gershman
@gershbrain.bsky.social
· Aug 4
Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience | Volume 32: The Handbook of Dopamine | ScienceDirect.com by Elsevier
Read the latest chapters of Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier’s leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature
www.sciencedirect.com
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Dan Goodman
@neural-reckoning.org
· Jul 11
Reposted by M Ganesh Kumar
Grace Lindsay
@neurograce.bsky.social
· Jul 23



![What do representations tell us about a system? Image of a mouse with a scope showing a vector of activity patterns, and a neural network with a vector of unit activity patterns
Common analyses of neural representations: Encoding models (relating activity to task features) drawing of an arrow from a trace saying [on_____on____] to a neuron and spike train. Comparing models via neural predictivity: comparing two neural networks by their R^2 to mouse brain activity. RSA: assessing brain-brain or model-brain correspondence using representational dissimilarity matrices](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:e6ewzleebkdi2y2bxhjxoknt/bafkreiav2io2ska33o4kizf57co5bboqyyfdpnozo2gxsicrfr5l7qzjcq@jpeg)





