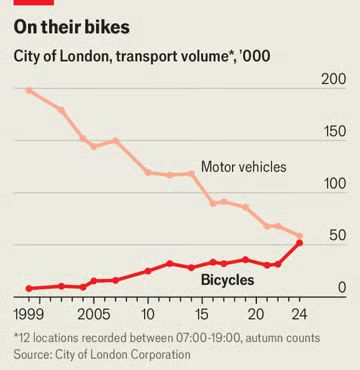
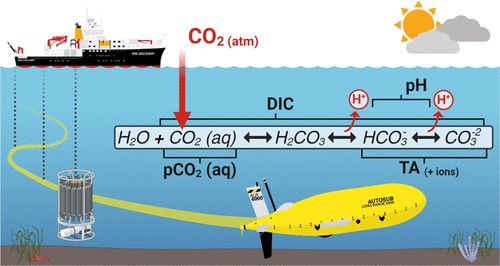
Julie Robidart
@robidart.bsky.social
280 followers
230 following
28 posts
Technological design to interpret signatures of ocean biology and biogeochemistry, at scale. Specialisation in omics, eDNA and microbiology
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Julie Robidart
@robidart.bsky.social
· May 27
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
John Timmer
@jtimmer.bsky.social
· Apr 29

AGU files new lawsuit to protect hundreds of thousands of federal workers
AGU and a coalition of plaintiffs have filed a complaint in a new lawsuit arguing President Donald J. Trump’s February Executive Order No. 14210 directing federal agencies to engage in “large-scale” r...
news.agu.org
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Ian Hall
@ianhall.bsky.social
· Apr 26

The world's biggest companies have caused $28 trillion in climate damage, a new study estimates
A new study estimates that the world’s biggest corporations have caused $28 trillion in climate damage, which is a shade less than the sum of all goods and services produced in the United States last ...
apnews.com
Julie Robidart
@robidart.bsky.social
· Apr 26
Howard Frumkin
@howardfrumkin.bsky.social
· Apr 26

Charting a path to health for all at net-zero emissions
Climate change is the defining health challenge of the 21st century, with record-breaking
temperatures and extreme weather events already exacting an unprecedented toll on
human health and wellbeing. ...
www.thelancet.com
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Reposted by Julie Robidart
Oded Rechavi
@odedrechavi.bsky.social
· Apr 4
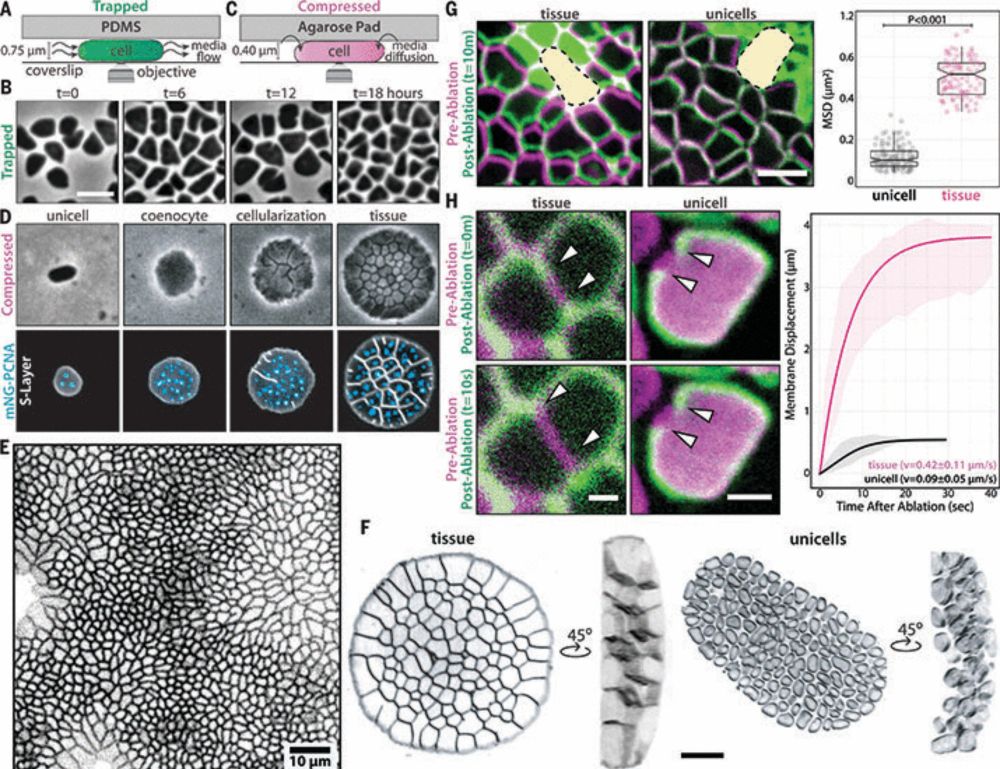
Tissue-like multicellular development triggered by mechanical compression in archaea
The advent of clonal multicellularity is a critical evolutionary milestone, seen often in eukaryotes, rarely in bacteria, and only once in archaea. We show that uniaxial compression induces clonal mul...
www.science.org