kevinbolding.bsky.social
@kevinbolding.bsky.social
420 followers
460 following
79 posts
Memory / olfaction PI at Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philly
boldinglab.org
[email protected]
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Julian Meeks
@meeksandmilds.bsky.social
· Jan 31
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Julian Meeks
@meeksandmilds.bsky.social
· Jan 31
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Adrien Peyrache
@apeyrache.bsky.social
· Jan 28

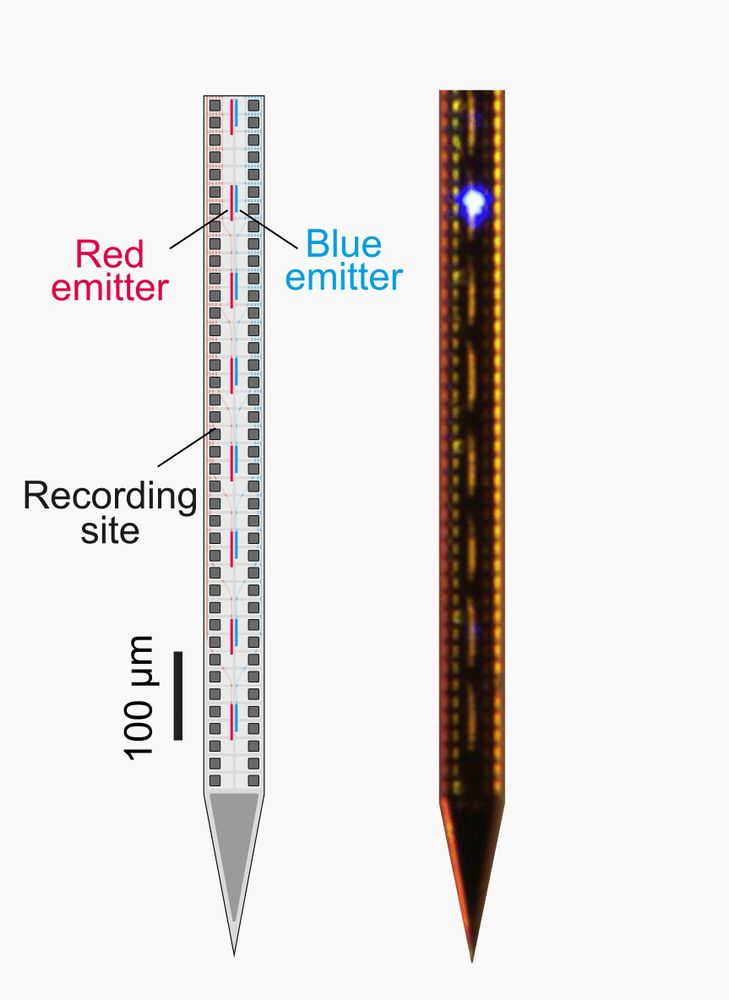
Latent learning drives sleep-dependent plasticity in distinct CA1 subpopulations
Guo et al. find that when mice repeatedly explore a novel environment, a distinct
subset of neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, which initially exhibits weak
spatial selectivity, gradually d...
www.cell.com
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Bob Pellegrino
@kingfunk.bsky.social
· Jan 26

The Effect of Olfactory Disorder (and Other Chemosensory Disorders) on Perception, Acceptance, and Consumption of Food
People with changes in the overall sensory experience of food often complain of taste disturbances, although the problem is normally caused by the loss of aroma in the food (thus an olfactory disorder...
link.springer.com
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Dayu Lin
@moccalin.bsky.social
· Jan 22
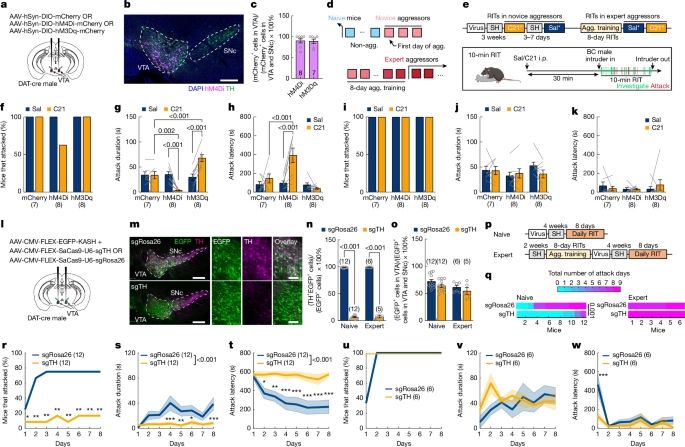
Experience-dependent dopamine modulation of male aggression - Nature
Dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area have a role in modulating aggression in adult male mice, and this effect of dopamine depends strongly on fighting experience.
www.nature.com
Reposted by kevinbolding.bsky.social
Dinu F Albeanu
@dinanthos.bsky.social
· Jan 23

Fast updating feedback from piriform cortex to the olfactory bulb relays multimodal identity and reward contingency signals during rule-reversal - Nature Communications
Hernandez-Trejo, Ciuparu, and Garcia da Silva et al. report that the piriform-to-olfactory bulb feedback in the mouse carries multimodal identity and reward contingency signals, which are re-formatted...
doi.org