Vijay Rathinam
@vijayrathinam.bsky.social
1K followers
230 following
45 posts
Professor of Immunology, UConn Health School of Medicine.
Studying innate immunity, infection and inflammation.
https://facultydirectory.uchc.edu/profile?profileId=Rathinam-Vijay2
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Jonathan Kagan
@jkagan1.bsky.social
· Sep 8

An NLRP3-stimulatory adjuvant improves the immunogenicity of influenza virus vaccines in mice and non-human primates | mBio
The generation of vaccines that stimulate T cell activities is an unmet need for the
scientific community, as T cells are the primary mediators of immune memory. In this
study, we report a new vaccine...
journals.asm.org
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Dr Rebecca Coll
@colllab.bsky.social
· Sep 2
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Vijay Rathinam
@vijayrathinam.bsky.social
· Aug 13
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Ivan Zanoni
@lozanzi.bsky.social
· Aug 6
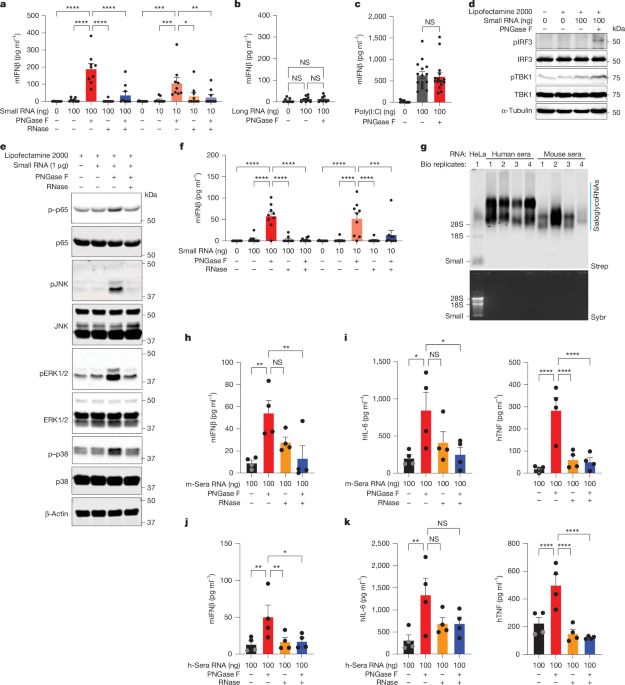
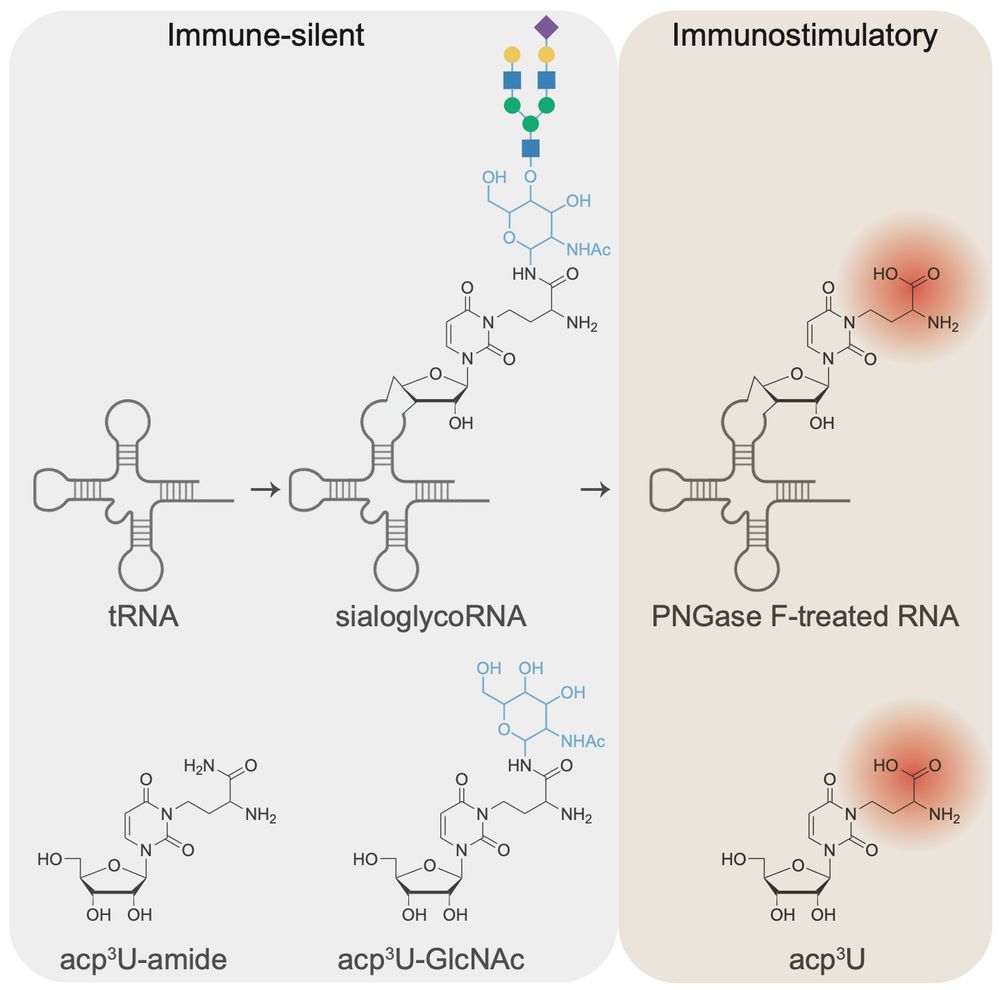
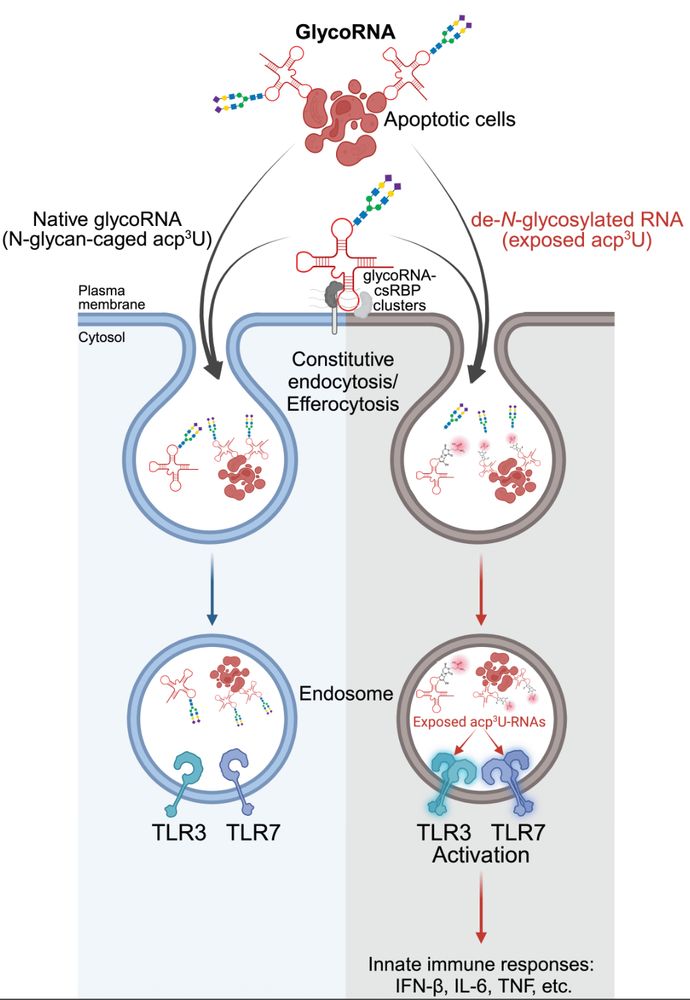
RNA N-glycosylation enables immune evasion and homeostatic efferocytosis - Nature
N-glycans on glycoRNAs prevent innate immune sensing of endogenous small RNAs, and the natural mechanism they use demonstrates how glycoRNAs exist on the cell surface and in the endosomal network with...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Ryan Flynn
@raflynn5.bsky.social
· Aug 6
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Ryan Flynn
@raflynn5.bsky.social
· Aug 6
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam
Reposted by Vijay Rathinam