Xiaoli Sky Wu
@xiaoliwu.bsky.social
370 followers
130 following
10 posts
Post doc with Mike E Greenberg at HMS, working on molecular neuroscience. Ph.D.at CSHL on identifying a novel family of cell type-specific cofactors. Co-organizer of Gene expression and RNA series, and Fragile nucleosome seminar.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Xiaoli Sky Wu
@xiaoliwu.bsky.social
· Jul 18
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Jackson Hoffman
@jxhoffman.bsky.social
· Jun 19
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Jeremy Berg
@jeremymberg.bsky.social
· Jun 16
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Jason Sheltzer
@jsheltzer.bsky.social
· May 23
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Immunity
@cp-immunity.bsky.social
· May 13
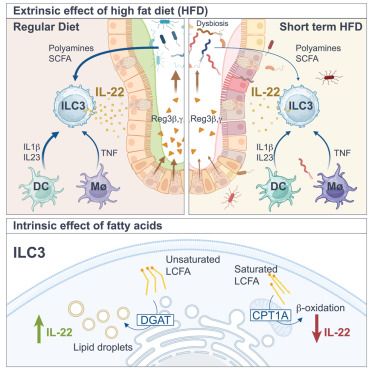
Acute exposure to high-fat diet impairs ILC3 functions and gut homeostasis
Xiong et al. report that short-term, high-fat diet exposure rapidly alters the gut microbial and immune environment, disrupting tissue homeostasis. IL-22 production by group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) is impaired, compromising gut barrier integrity. Saturated fatty acids intrinsically suppress ILC3 function, reducing their ability to control gut inflammation.
dlvr.it
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Janet Song
@janetsong.bsky.social
· Apr 2

Human-chimpanzee tetraploid system defines mechanisms of species-specific neural gene regulation
A major challenge in human evolutionary biology is to pinpoint genetic differences that underlie human-specific traits, such as increased neuron number and differences in cognitive behaviors. We used human-chimpanzee tetraploid cells to distinguish gene expression changes due to cis -acting sequence variants that change local gene regulation, from trans expression changes due to species differences in the cellular environment. In neural progenitor cells, examination of both cis and trans changes – combined with CRISPR inhibition and transcription factor motif analyses – identified cis -acting, species-specific gene regulatory changes, including to TNIK , FOSL2 , and MAZ , with widespread trans effects on neurogenesis-related gene programs. In excitatory neurons, we identified POU3F2 as a key cis -regulated gene with trans effects on synaptic gene expression and neuronal firing. This study identifies cis -acting genomic changes that cause cascading trans gene regulatory effects to contribute to human neural specializations, and provides a general framework for discovering genetic differences underlying human traits. ### Competing Interest Statement C.A.W. is on the SAB of Bioskyrb Genomics (cash, equity) and Mosaica Therapeutics (cash, equity), and is an advisor to Maze Therapeutics (equity), but these have no relevance to this work. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
www.biorxiv.org
Xiaoli Sky Wu
@xiaoliwu.bsky.social
· Apr 2

Human-chimpanzee tetraploid system defines mechanisms of species-specific neural gene regulation
A major challenge in human evolutionary biology is to pinpoint genetic differences that underlie human-specific traits, such as increased neuron number and differences in cognitive behaviors. We used ...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu
Reposted by Xiaoli Sky Wu