
X/Twitter: https://x.com/ssingha9956
#MicroSky 🖥️🧬🦠
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
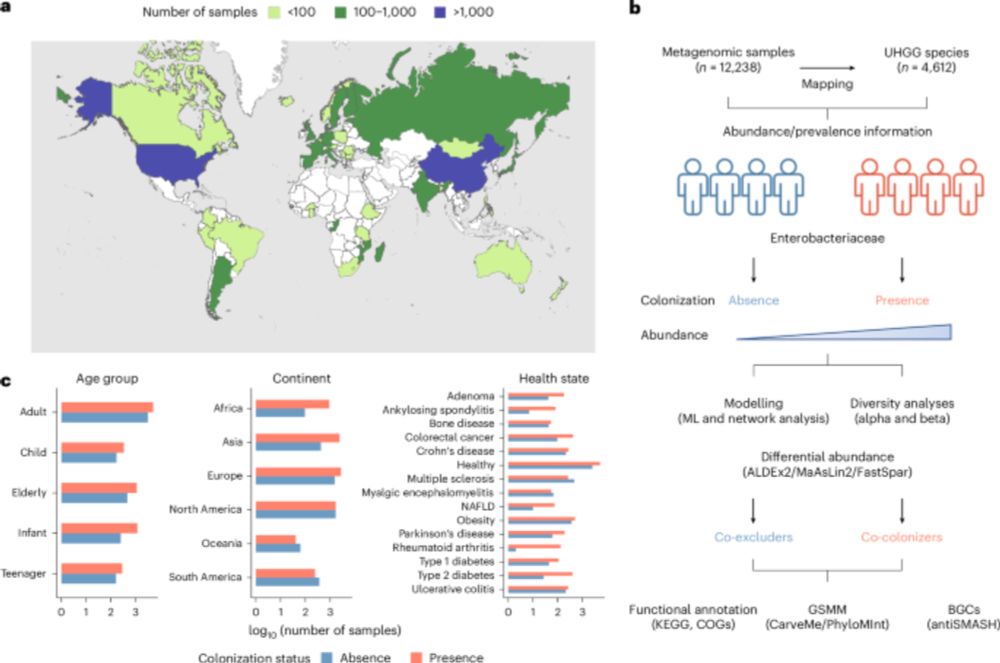
In this study, we present the largest systematic analysis of microbiome structure and function, integrating 85K uniformly processed metagenomes from diverse habitats worldwide.
@podlesny.bsky.social @jonas-bio.bsky.social @borklab.bsky.social

#MicroSky 🖥️🧬🦠
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
About 15,000 pairwise interactions within S. epidermidis from 18 people in 6 families reveal the antagonism and molecular trade-offs that shape the skin microbiota @contaminatedsci.bsky.social @mancusosci.bsky.social #MicrobiomeSky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
read here: rdcu.be/et7VP
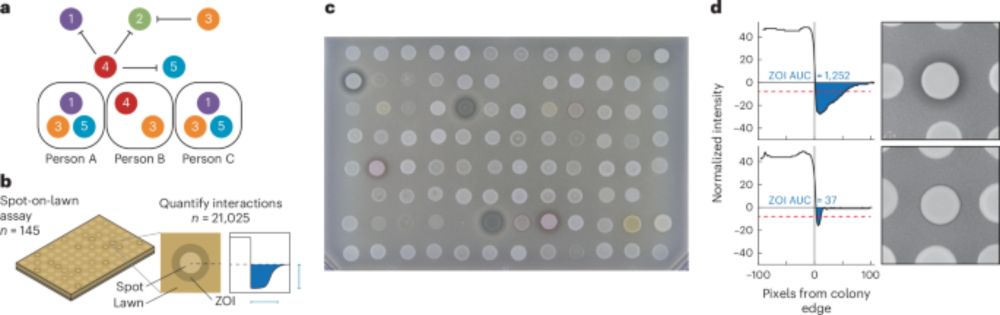
About 15,000 pairwise interactions within S. epidermidis from 18 people in 6 families reveal the antagonism and molecular trade-offs that shape the skin microbiota @contaminatedsci.bsky.social @mancusosci.bsky.social #MicrobiomeSky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
read here: rdcu.be/et7VP

rdcu.be/epoRR
@blekhman.bsky.social @sambhawa.bsky.social and Dr. Kelsey Johnson.
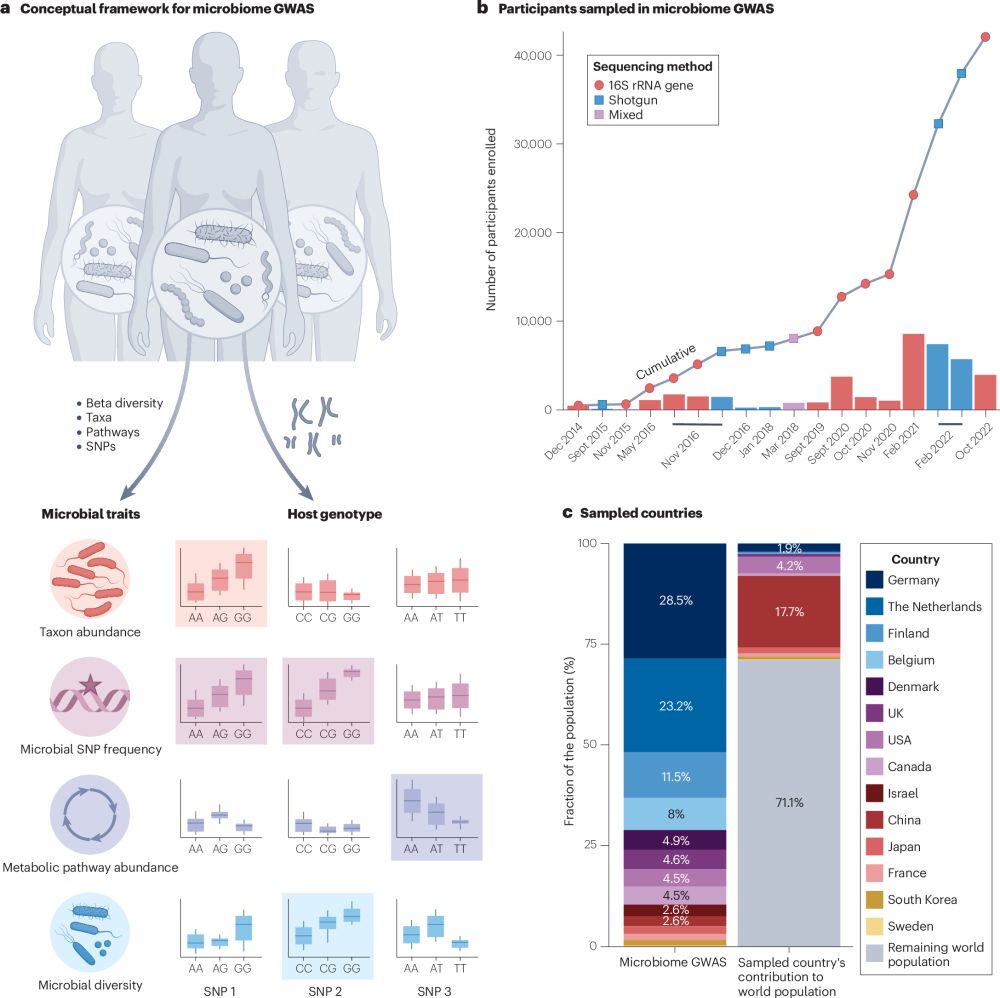
rdcu.be/epoRR
@blekhman.bsky.social @sambhawa.bsky.social and Dr. Kelsey Johnson.
Here is my article on page 43:
online.fliphtml5.com/dqwze/jzki/

Here is my article on page 43:
online.fliphtml5.com/dqwze/jzki/
@gibbological.bsky.social @cdiener.com
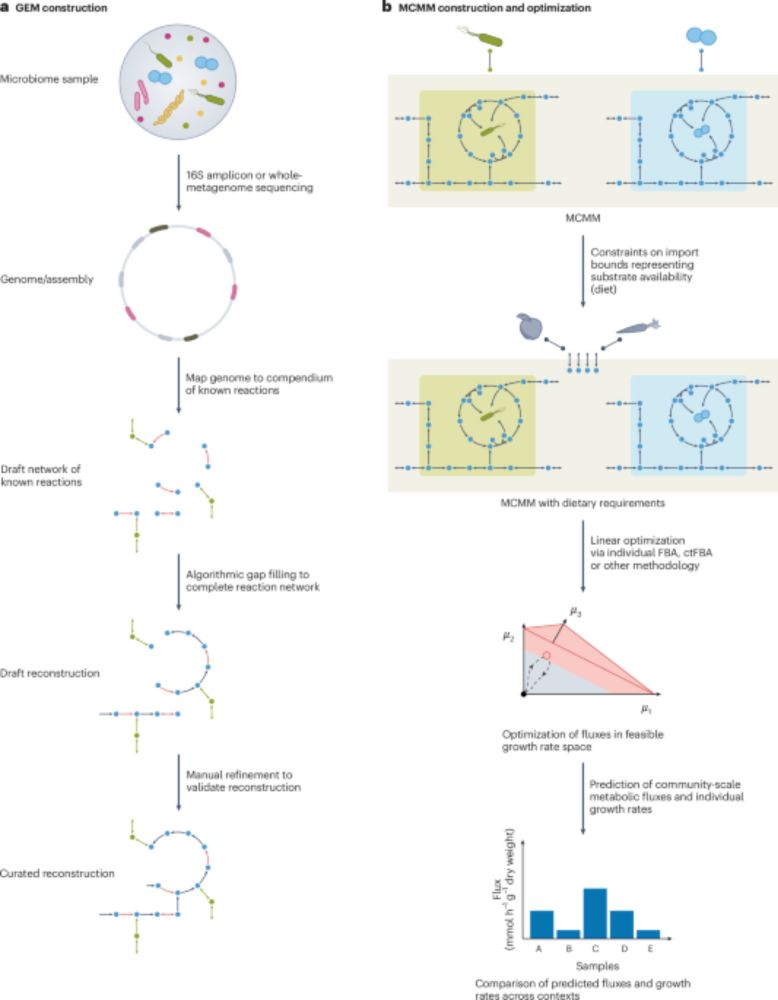
@gibbological.bsky.social @cdiener.com
openrxiv.org/introducing-...
@openrxiv.bsky.social

openrxiv.org/introducing-...
@openrxiv.bsky.social

Feat. @lorenzspreen.bsky.social @carlbergstrom.com @jbakcoleman.bsky.social and others, as well as my efforts to monitor and analyze the network out of the equilibrium regime 👇
www.science.org/content/arti...

Feat. @lorenzspreen.bsky.social @carlbergstrom.com @jbakcoleman.bsky.social and others, as well as my efforts to monitor and analyze the network out of the equilibrium regime 👇
www.science.org/content/arti...
Are you looking forward to 2025 as much as we are? 👀
We just updated our 2025 Annual Poster to include even more events for you to join, so go and have a look!
➡️ s.embl.org/poster-bl
#EMBLEvents #molecularbiology #lifesciencetraining

Are you looking forward to 2025 as much as we are? 👀
We just updated our 2025 Annual Poster to include even more events for you to join, so go and have a look!
➡️ s.embl.org/poster-bl
#EMBLEvents #molecularbiology #lifesciencetraining
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@archaeal.bsky.social @quendi.bsky.social @robinrohwer.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@archaeal.bsky.social @quendi.bsky.social @robinrohwer.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Thank you, 2024, for the lessons, connections, and growth.
This year, I’m looking forward to new opportunities, achieving career goals, advancing microbiome research, and collaborating on groundbreaking ideas. Let’s make 2025 unforgettable!
#NewYear #Grateful #Microbiome #Innovation
Thank you, 2024, for the lessons, connections, and growth.
This year, I’m looking forward to new opportunities, achieving career goals, advancing microbiome research, and collaborating on groundbreaking ideas. Let’s make 2025 unforgettable!
#NewYear #Grateful #Microbiome #Innovation

