Nicole Messina
@nicolemessina.bsky.social
230 followers
100 following
10 posts
Immunologist interested in immunoregulation, vaccines, paediatric immunology and disease risk. #TB #ID #ImmunoSky
https://www.mcri.edu.au/researcher-details/nicole-messina
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Gabriele Pollara
@gpollara.bsky.social
· Apr 21
Mahdad Noursadeghi
@mnoursad.bsky.social
· Apr 21

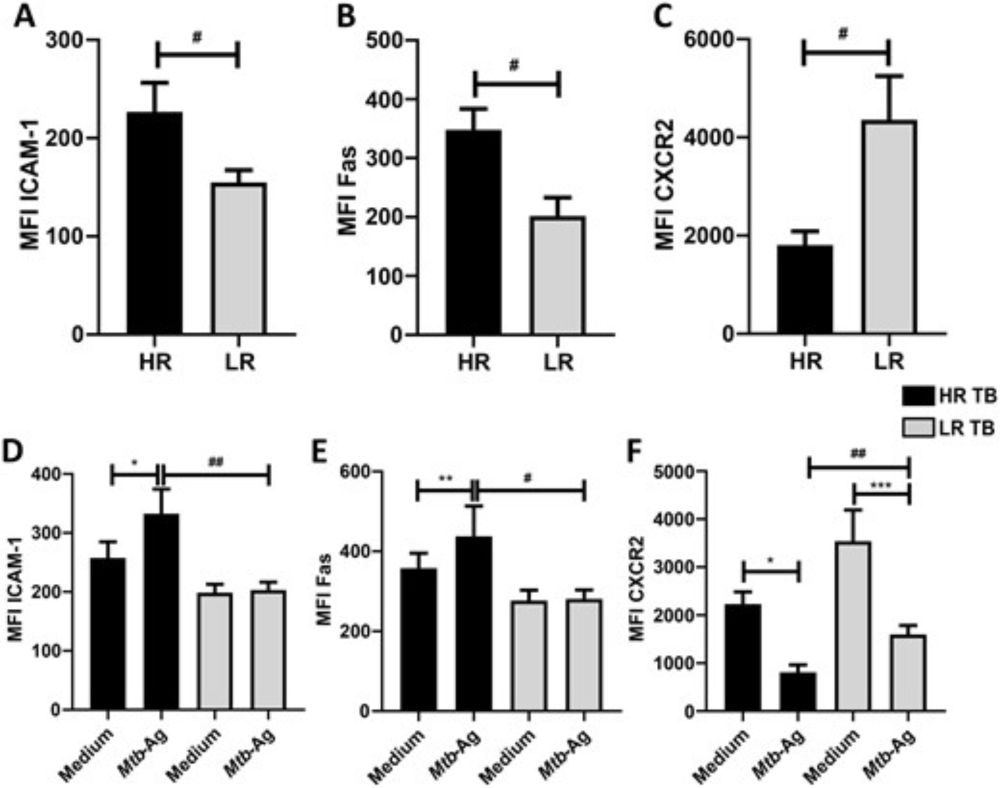
Evolution of T cell responses in the tuberculin skin test reveals generalisable Mtb-reactive T cell metaclones.
T cells contribute to immune protection and pathogenesis in tuberculosis, but measurements of polyclonal responses have failed to resolve correlates of outcome. We report the first temporal…
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Ivan Zanoni
@lozanzi.bsky.social
· Mar 15
Transient inhibition of type I interferon enhances CD8+ T cell stemness and vaccine protection | Journal of Experimental Medicine | Rockefeller University Press
Broomfield et al. demonstrate that early type I interferon blockade alters CXCR3 chemokine regulation and cell location to promote an antigen-dependent CD8
rupress.org
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Marc Veldhoen
@marcveld.bsky.social
· Jan 22

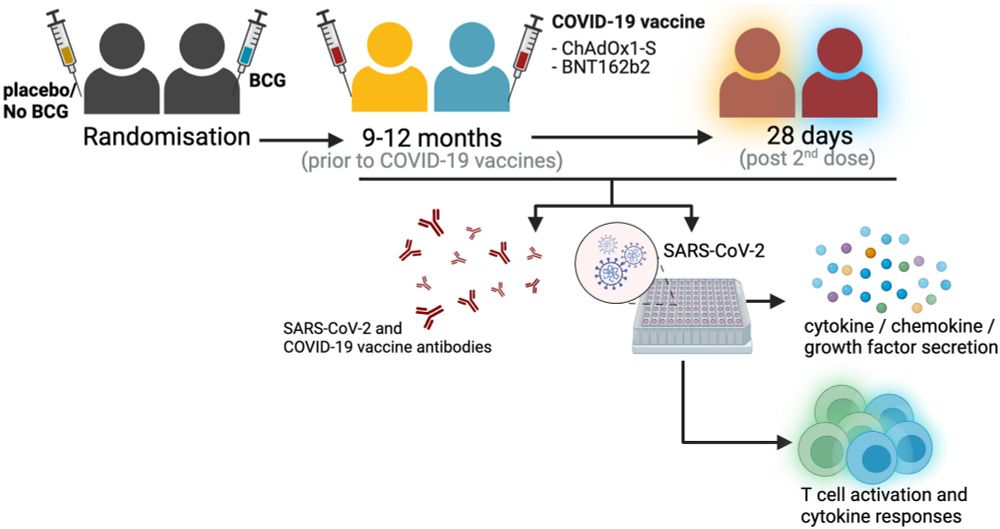
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody specificities differ dramatically between recently infected infants and immune-imprinted individuals
The immune response to viral infection is shaped by past exposures to related virus strains, a phenomenon known as imprinting. For SARS-CoV-2, much of the population has been imprinted by a viral spike from an early strain, either through vaccination or infection during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence of this imprinting, infection with more recent SARS-CoV-2 strains primarily boosts cross-reactive antibodies elicited by the imprinting strain. Here we compare the neutralizing antibody specificities of imprinted individuals versus infants infected with a recent strain. Specifically, we use pseudovirus-based deep mutational scanning to measure how spike mutations affect neutralization by the serum antibodies of adults and children imprinted by the original vaccine versus infants with a primary infection by a XBB* variant. While the serum neutralizing activity of the imprinted individuals primarily targets the spike receptor-binding domain (RBD), serum neutralizing activity of infants only infected with XBB* mostly targets the spike N-terminal domain (NTD). In these infants, secondary exposure to the XBB* spike via vaccination shifts more of the neutralizing activity towards the RBD, although the specific RBD sites targeted are different than for imprinted adults. The dramatic differences in neutralization specificities among individuals with different exposure histories likely impact SARS-CoV-2 evolution.
### Competing Interest Statement
J.D.B. and B.D. are inventors on Fred Hutch licensed patents related to the pseudovirus deep mutational scanning technique used in this paper. J.D.B. consults for Apriori Bio, Invivyd, Pfizer, the Vaccine Company, Moderna, and GSK. B.D. consults for Moderna. HYC has consulted for Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Ellume, and has served on advisory boards for Vir, Merck, Roche and Abbvie. She has received research funding from Gates Ventures. M.A.S. has received research funding from Cepheid and Pfizer and has consulted for Merck.
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Gabriele Pollara
@gpollara.bsky.social
· Nov 25

Genetically diverse Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates manipulate inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion independently of macrophage metabolic rewiring
The glycolytic pathway is required for maximum IL-1β production by macrophages infected with live distinct M. tuberculosis isolates, but mitochondria metab
academic.oup.com
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Nicole Messina
@nicolemessina.bsky.social
· Nov 29
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Reposted by Nicole Messina
Dr. Amy Lee
@minisciencegirl.bsky.social
· Nov 21
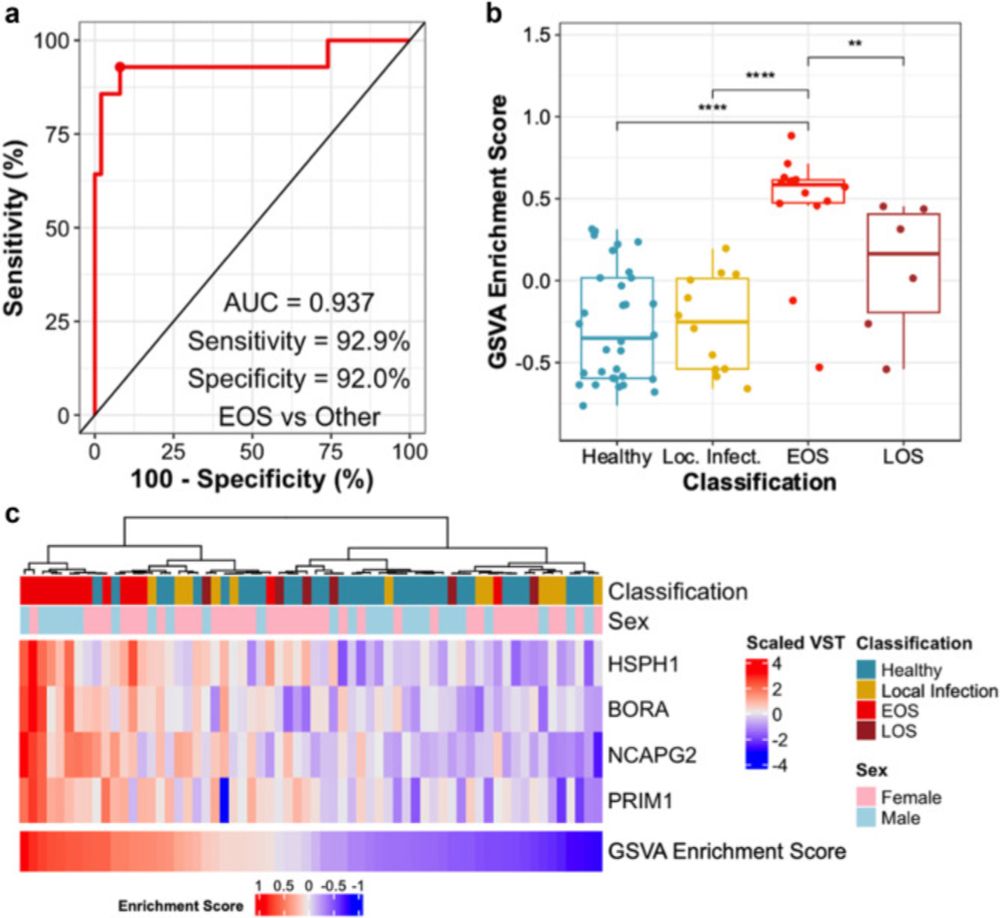
Predictive gene expression signature diagnoses neonatal sepsis before clinical presentation
Despite appearing healthy at birth, neonates who later developed EOS already had distinct
whole blood gene expression changes at birth, which enabled the development of a 4-gene
predictive signature f...
www.thelancet.com
Nicole Messina
@nicolemessina.bsky.social
· Nov 19

Antecedent and persistent symptoms in COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses: Insights from prospectively collected data in the BRACE trial
Healthcare workers with COVID-19 were more likely to have severe and longer-lasting
symptoms than those with a non-COVID-19 respiratory illness, with a higher proportion
meeting the WHO or NICE defini...
www.journalofinfection.com