Chris Lapointe
@lapointelab.bsky.social
460 followers
440 following
4 posts
RNA biochemistry | Translational control | Single-molecule approaches | Dogs | Cycling. Assistant Professor, Basic Sciences Division, Fred Hutch
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Subramaniam Lab
@rasilab.bsky.social
· May 2

Deaminase-based RNA recording enables high throughput mutational profiling of protein-RNA interactions
Protein-RNA interactions govern nearly every aspect of RNA metabolism and are frequently dysregulated in disease. While individual protein residues and RNA nucleotides critical for these interactions ...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Subramaniam Lab
@rasilab.bsky.social
· May 2

Deaminase-based RNA recording enables high throughput mutational profiling of protein-RNA interactions
Protein-RNA interactions govern nearly every aspect of RNA metabolism and are frequently dysregulated in disease. While individual protein residues and RNA nucleotides critical for these interactions ...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Shicheng Guo
@shihcheng.bsky.social
· Apr 3
Complex water networks visualized by cryogenic electron microscopy of RNA | Nature
The stability and function of biomolecules are directly influenced by their myriad interactions with water1–16. In this study, we investigated water through cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) on a highly solvated molecule, the Tetrahymena ribozyme, determined at 2.2 and 2.3 Å resolutions. By employing segmentation-guided water and ion modeling (SWIM)17,18, an approach combining resolvability and chemical parameters, we automatically modeled and cross-validated water molecules and Mg2+ ions in the ribozyme core, revealing the extensive involvement of water in mediating RNA non-canonical interactions. Unexpectedly, in regions where SWIM does not model ordered water, we observed highly similar densities in both cryo-EM maps. In many of these regions, the cryo-EM densities superimpose with complex water networks predicted by molecular dynamics (MD), supporting their assignment as water and suggesting a biophysical explanation for their elusiveness to conventional atomic coordinate mod
doi.org
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Edward Wallace
@ewjwallace.bsky.social
· Apr 22
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Kurianlab
@kurianlab.bsky.social
· Apr 19
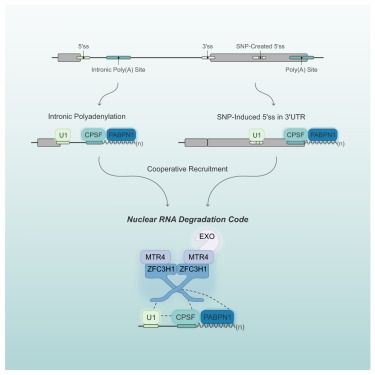
A nuclear RNA degradation code is recognized by PAXT for eukaryotic transcriptome surveillance
Soles et al. demonstrate that the combination of a 5′ splice site and a poly(A) junction
constitutes a nuclear RNA degradation code that targets RNAs for degradation by the
PAXT adaptor and the RNA ex...
www.cell.com
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Mark Dawson
@mafdawson.bsky.social
· Jan 2
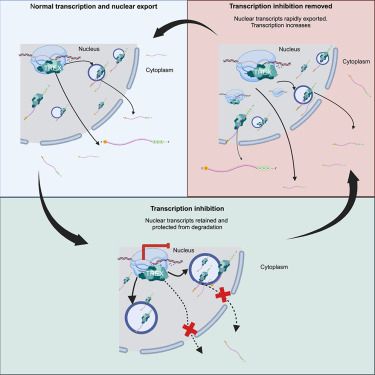
mRNA export factors store nascent transcripts within nuclear speckles as an adaptive response to transient global inhibition of transcription
Transcription inhibitors also disrupt nuclear export. Here, Williams et al. reveal that mRNA export factors sense transcription inhibition and adapt by storing mature export-competent mRNA in nuclear speckles. This enables rapid release when transcription resumes and ensures retention of cellular identity and viability during a transient global transcription insult.
www.cell.com
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Nikos Kouvelas
@nickkouvelas.bsky.social
· Apr 17
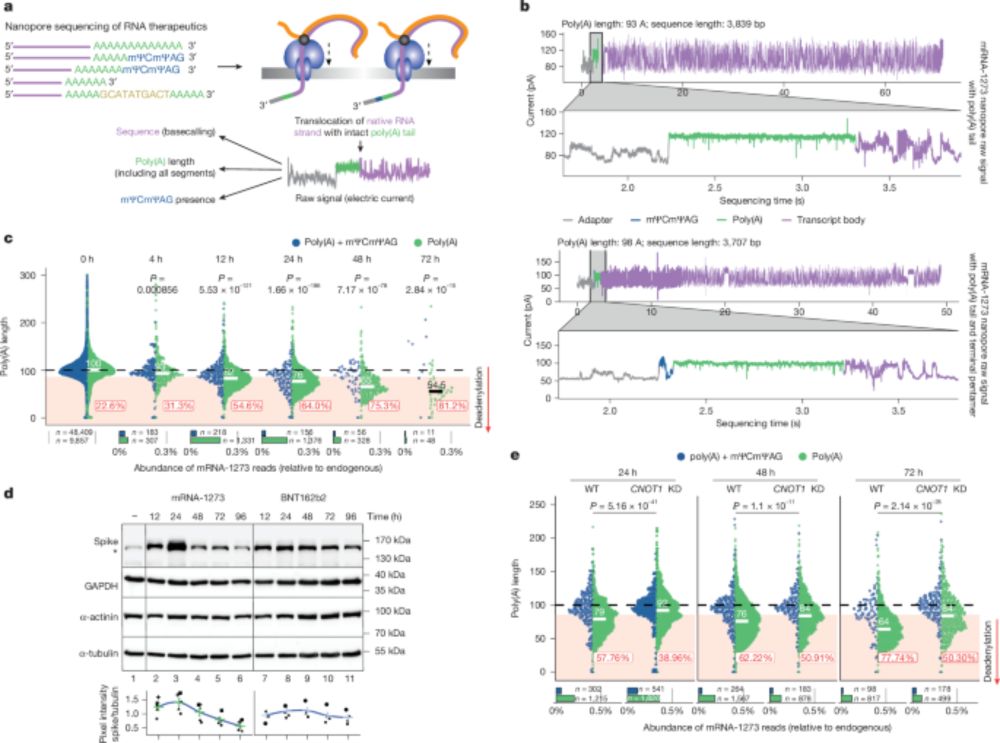
Re-adenylation by TENT5A enhances efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines - Nature
Upon intramuscular administration, COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are primarily taken up by macrophages, in which the cellular machinery extends their poly(A) tails, thereby increasing mRNA stability and tran...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Fred Hutch
@fredhutch.org
· Apr 16

Rewriting the story about the molecules that turn genes on and off
A study by researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center published in Nature revises the standard story about transcription factors binding close to the genes they regulate. That is true only for a small su...
www.fredhutch.org
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Eugene Valkov
@eugenevalkov.bsky.social
· Apr 16
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Sue Biggins
@suebiggins.bsky.social
· Apr 16
Fred Hutch
@fredhutch.org
· Apr 16

Rewriting the story about the molecules that turn genes on and off
A study by researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center published in Nature revises the standard story about transcription factors binding close to the genes they regulate. That is true only for a small su...
www.fredhutch.org
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Billy Li
@dsrna.bsky.social
· Apr 15
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Kurianlab
@kurianlab.bsky.social
· Apr 16
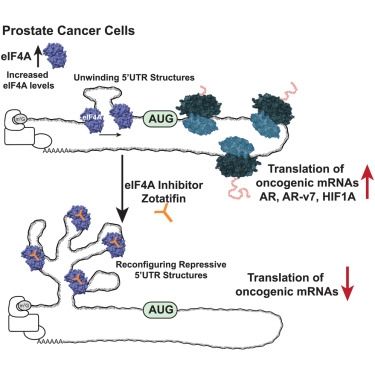
Small-molecule RNA therapeutics to target prostate cancer
Kuzuoglu-Ozturk et al. showcase a therapeutic approach, “translatome therapy,” to
combat lethal prostate cancer. Zotatifin, a clinical molecule, targets the RNA-helicase
eIF4A. Zotatifin decreases the...
www.cell.com
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Vijay Ramani
@vram142.bsky.social
· Apr 16
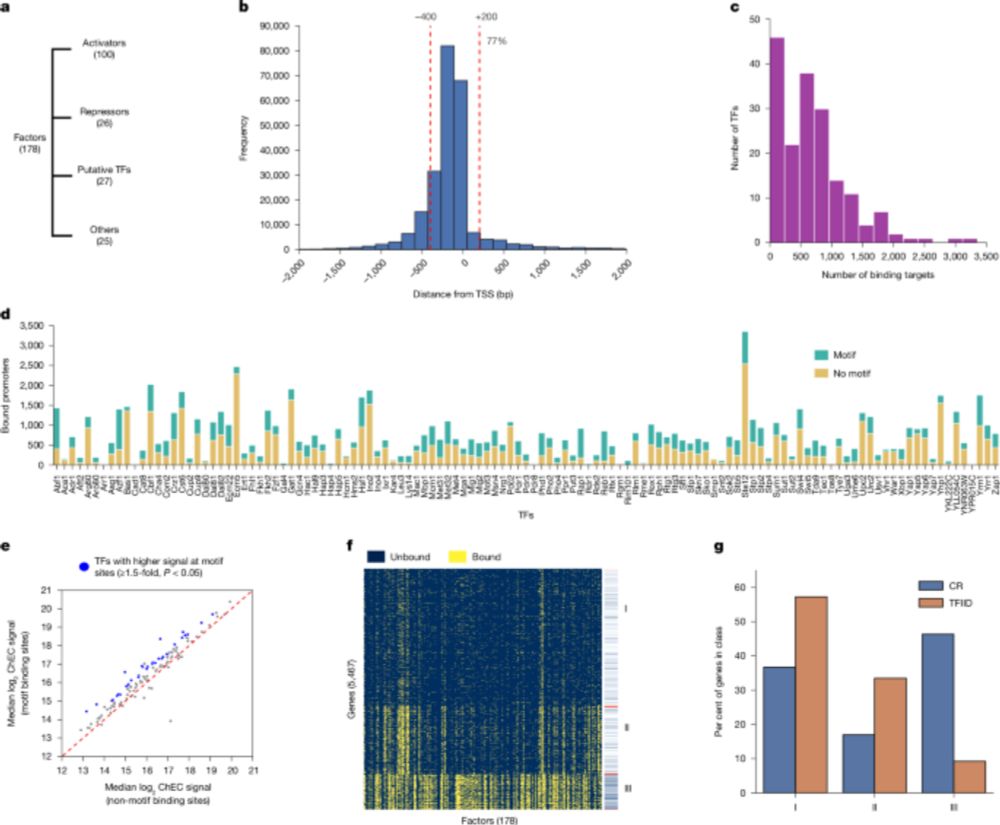
Low overlap of transcription factor DNA binding and regulatory targets - Nature
A near-complete survey of transcription factor activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals that most transcription factors have both activator and repressor activities and limited overlap between t...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Reposted by Chris Lapointe
Michael Kearse
@michaelkearse.bsky.social
· Apr 12