Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
680 followers
260 following
12 posts
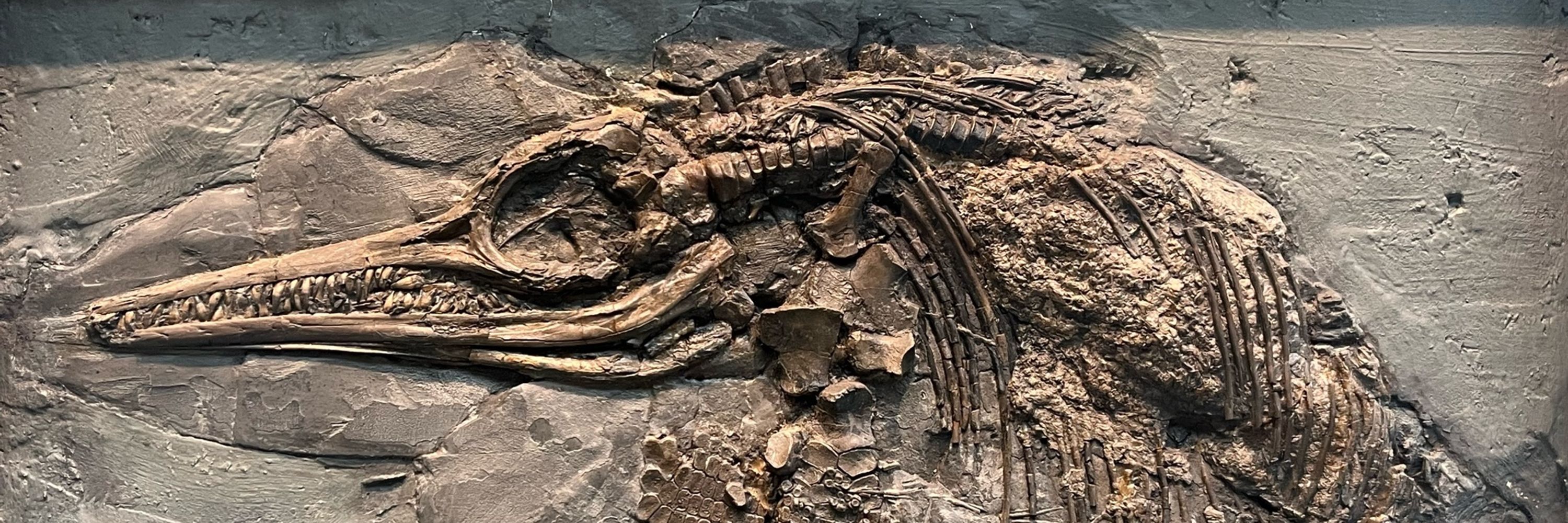
Group leader at the University of Birmingham interested in rare diseases caused by inherited defects in DNA repair and replication. Amateur geologist/palaeontologist and shark enthusiast.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Niels Keijzer
@nkeijzer.bsky.social
· Jul 31
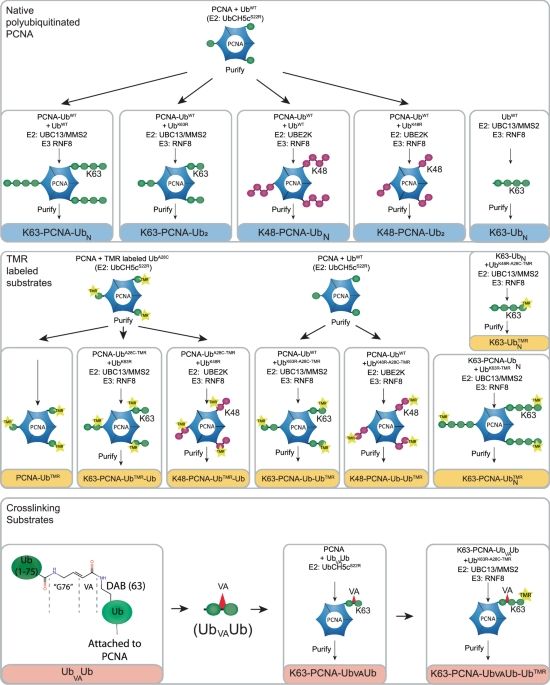
USP1/UAF1 targets polyubiquitinated PCNA with an exo-cleavage mechanism that can temporarily enrich for monoubiquitinated PCNA - Nature Communications
DNA damage tolerance is regulated by ubiquitination of PCNA. Here, the authors present kinetic and structural studies showing that USP1/UAF1 prefers trimming K63- and K48-ubiquitin chains down over cl...
doi.org
Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
· Jul 11
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Molecular Cell
@cp-molcell.bsky.social
· Jun 26
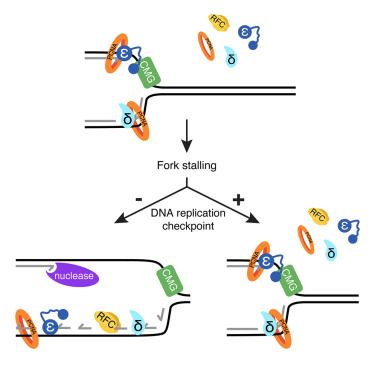
The DNA replication checkpoint limits Okazaki fragment accumulation to protect and restart stalled forks
Canal et al. used biochemical reconstitution of DNA replication to show that continued Okazaki fragment synthesis after nucleotide exhaustion depletes PCNA, RFC, and DNA polymerases ε and δ, deprotecting replication forks and impairing restart. By limiting Okazaki fragment generation and factor depletion, the replication checkpoint protects forks, allows restart, and promotes survival.
dlvr.it
Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
· Jun 18

USP37 prevents premature disassembly of stressed replisomes by TRAIP - Nature Communications
The replicative helicase CMG is targeted for removal or proteolysis by the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAIP. This study describes how the de-ubiquitylating enzyme USP37 protects genome stability by preventin...
www.nature.com
Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
· Jun 12
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Cell Reports
@cp-cellreports.bsky.social
· May 27
USP37 protects mammalian cells during DNA replication stress by counteracting CUL2LRR1 and TRAIP
Villa et al. show that the USP37 deubiquitylase is tethered to the CMG helicase at DNA replication forks in mammalian cells. USP37 protects cells during DNA replication stress by counteracting two replisome-coupled ubiquitin ligases. USP37 counteracts CUL2LRR1 during DNA synthesis defects and opposes TRAIP in response to topological stress.
dlvr.it
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Boulton Lab
@boultonlab.bsky.social
· May 27
Reposted by Grant Stewart
The Downs Lab
@thedownslab.bsky.social
· May 27

ARID1A stabilises non-homologous end joining factors at DNA breaks induced by the G4 ligand pyridostatin
ARID1A is a subunit of the BAF chromatin remodelling complex that is frequently mutated in cancer. It is challenging to predict how ARID1A loss impacts cancer therapy response because it participates ...
www.biorxiv.org
Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
· May 14

Inherited deficiency of DIAPH1 identifies a DNA double strand break repair pathway regulated by γ-actin - Nature Communications
DNA double strand break repair pathways ensure genome stability and prevent disease. Here the authors show that the actin nucleating factor DIAPH1 and γ-actin promote homologous recombination (HR)-dep...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Grant Stewart
JStark lab
@jstarklab.bsky.social
· May 12

53BP1/RIF1 and DNA-PKcs show distinct genetic interactions with diverse chromosomal break repair outcomes.
DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are the effective lesion of cancer radiotherapy and induce gene editing. 53BP1 accumulates at DSBs and is implicated in end joining (EJ) repair, but its influence on DS...
www.biorxiv.org
Grant Stewart
@profstewartlab.bsky.social
· Apr 15
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Reposted by Grant Stewart
Cantorlab
@cantorlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
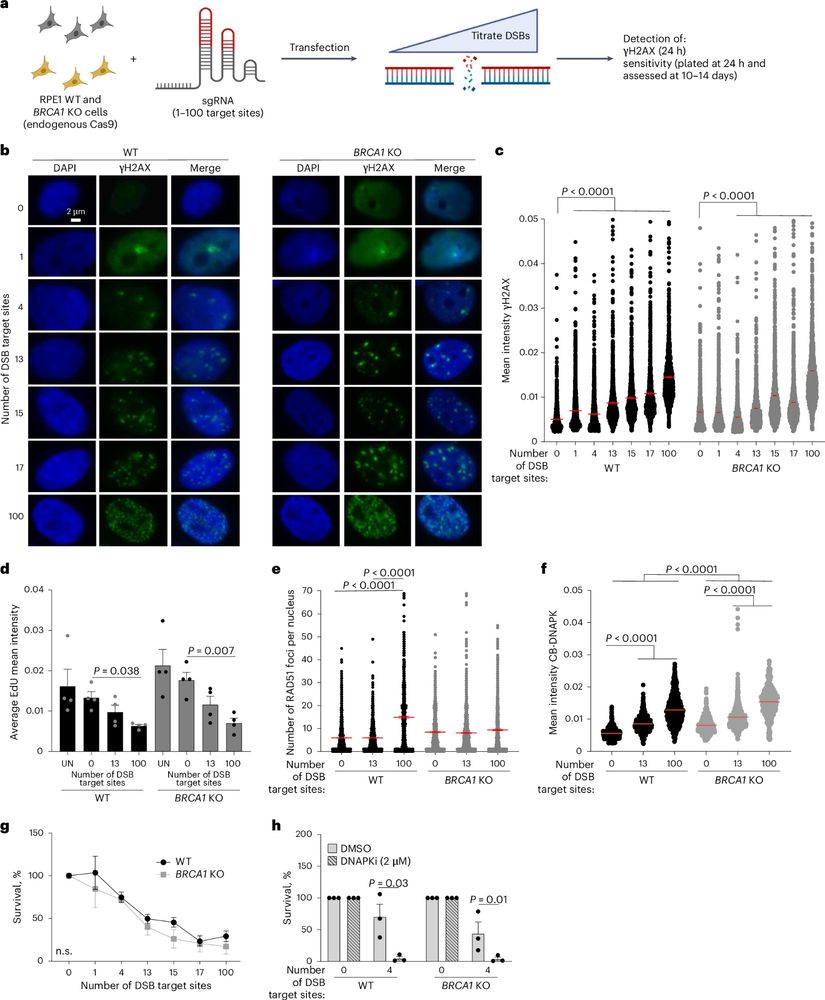
Targeting BRCA1-deficient PARP inhibitor-resistant cells with nickases reveals nick resection as a cancer vulnerability
Nature Cancer - Whalen et al. report that increased DNA end resection in BRCA-deficient, PARP inhibitor-resistant cancers leads to increased sensitivity to DNA nicks, limiting tumor formation in...
rdcu.be