Josh Riback
@superscijew.bsky.social
600 followers
270 following
9 posts
Assistant professor @BCMHouston. Interested in IDPs, RNPs, and condensates in cells viewed from biophysical chemistry and polymer biophysics. www.RibackLab.com
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Reposted by Josh Riback
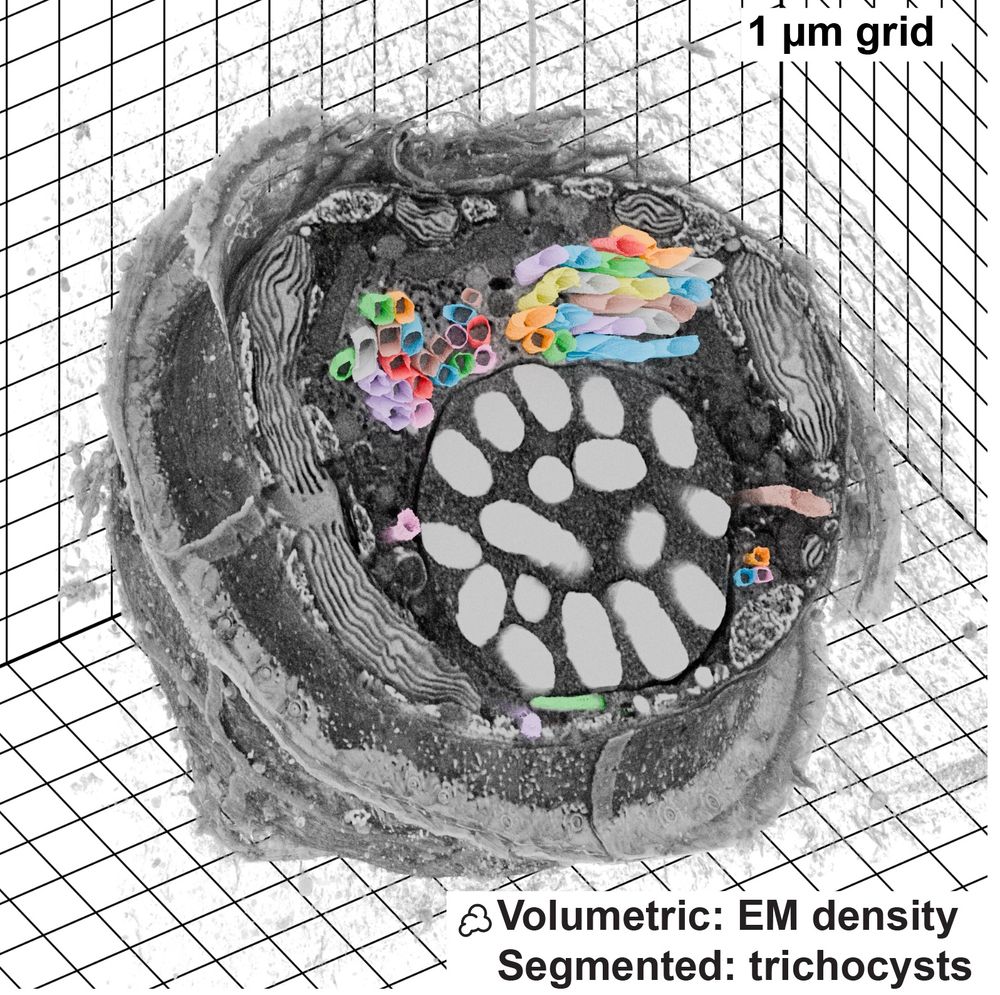
Brugues Lab
@brugueslab.bsky.social
· Sep 3
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
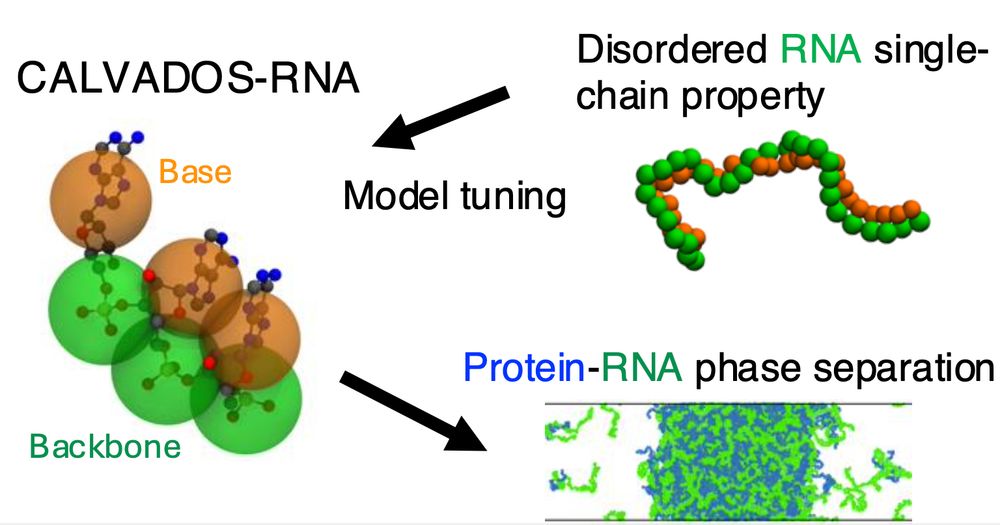
Alex Holehouse
@alexholehouse.bsky.social
· May 23
Reposted by Josh Riback
Mary Mirvis
@marymirvis.bsky.social
· Apr 19

A scoping study of the whole-cell imaging literature: a foundational corpus, potential for mesoscale data synthesis, and implications for standardization of an emerging field
The level of cellular organization bridging the mesoscale and whole-cell scale is coming into focus as a new frontier in cell biology. Great progress has been made in unraveling the complex physical a...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Josh Riback
Josh Riback
@superscijew.bsky.social
· Feb 28
Josh Riback
@superscijew.bsky.social
· Feb 28
Josh Riback
@superscijew.bsky.social
· Feb 28
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
Philip Ball
@philipcball.bsky.social
· Jan 16
Reposted by Josh Riback
Reposted by Josh Riback
SpruijtLab
@spruijtlab.bsky.social
· Jan 13

Selective ion binding and uptake shape the microenvironment of biomolecular condensates
Biomolecular condensates modulate various ion-dependent cellular processes and can regulate subcellular ion distributions by selective uptake of ions. However, the molecular grammar governing condensa...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Josh Riback
Joe Rogers
@josephrogers.bsky.social
· Jan 13

Proteome-scale quantification of the interactions driving condensate formation of intrinsically disordered proteins
The formation of biomolecular condensates is involved in compartmentalisation, regulation, and signalling across most living organisms. Condensation can be driven by phase separation of proteins, and ...
doi.org