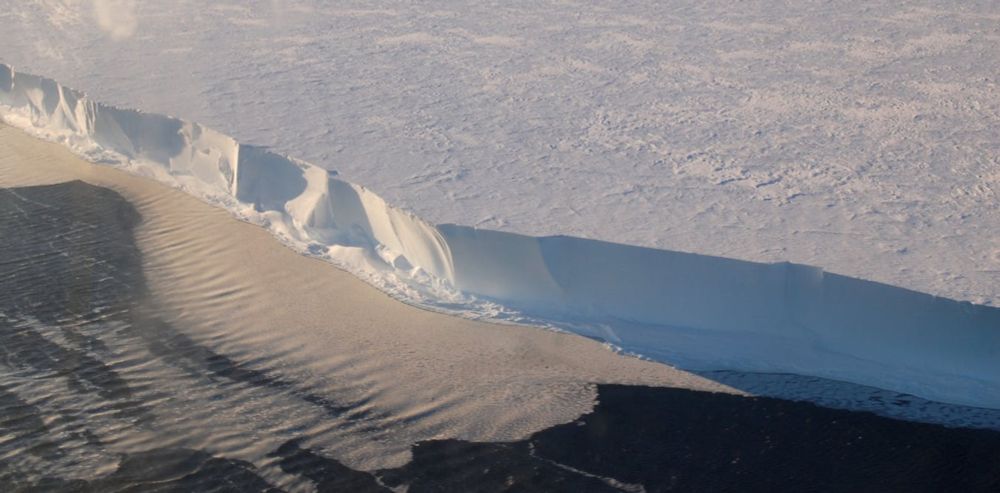
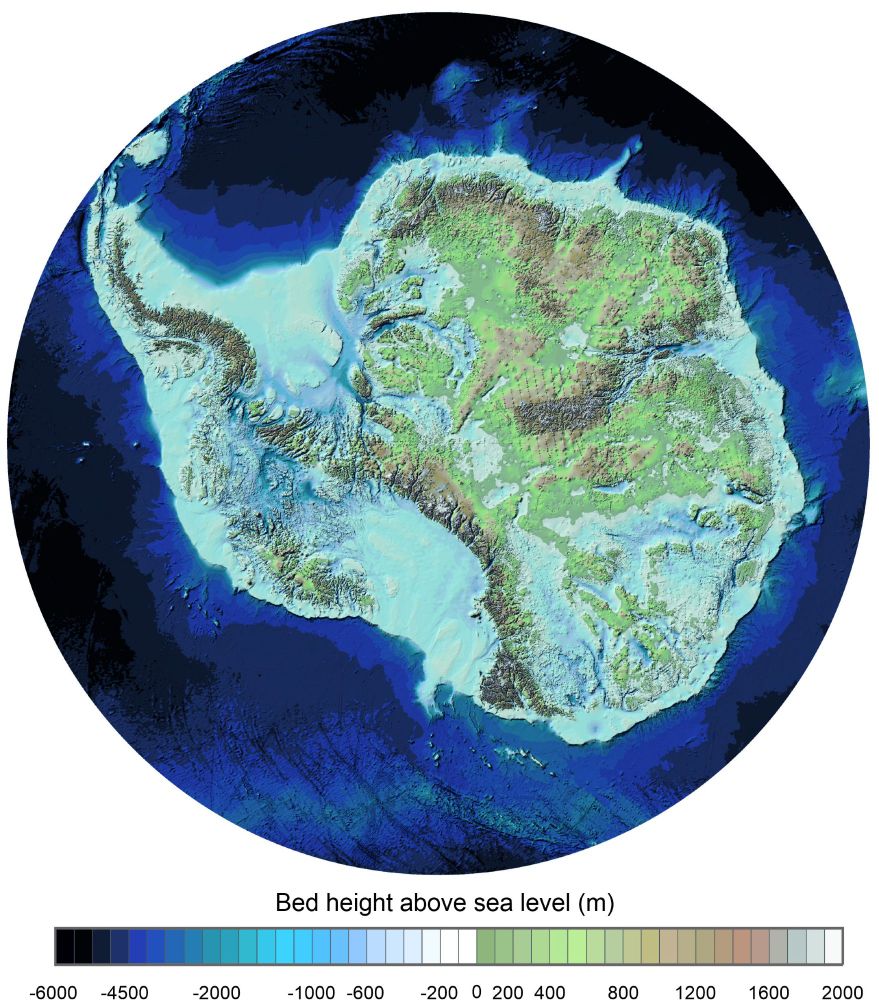
tamino.wordpress.com/2025/08/03/s...
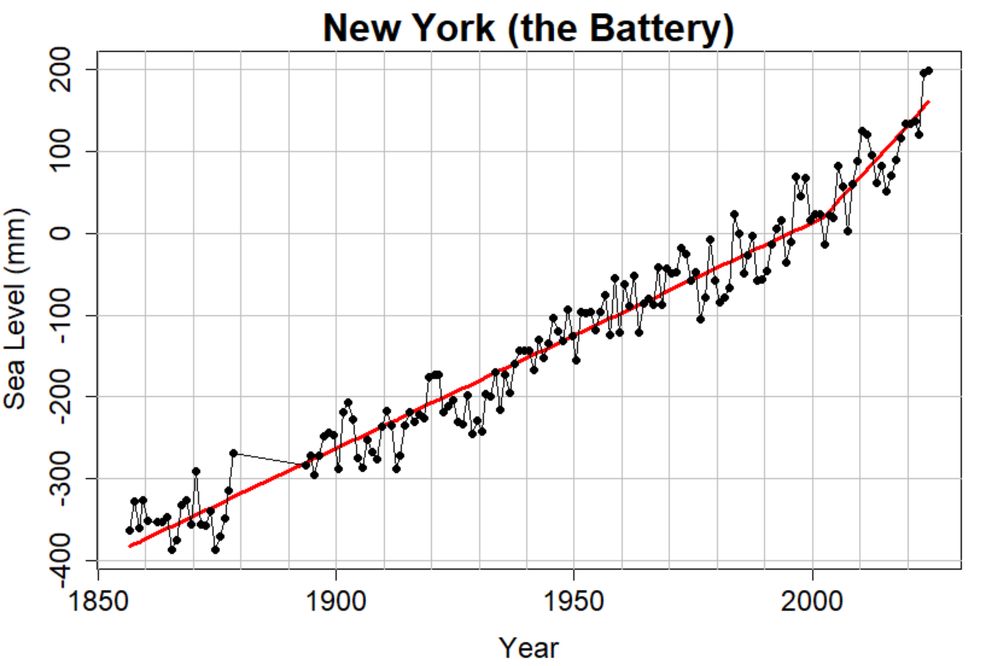
Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
community to be in 2073?
Some context: The Karthaus summer school is an occasion where parts of our research community comes together — In 2023, I was lucky to participate myself and it was the year in which a new workshop was included in the program.

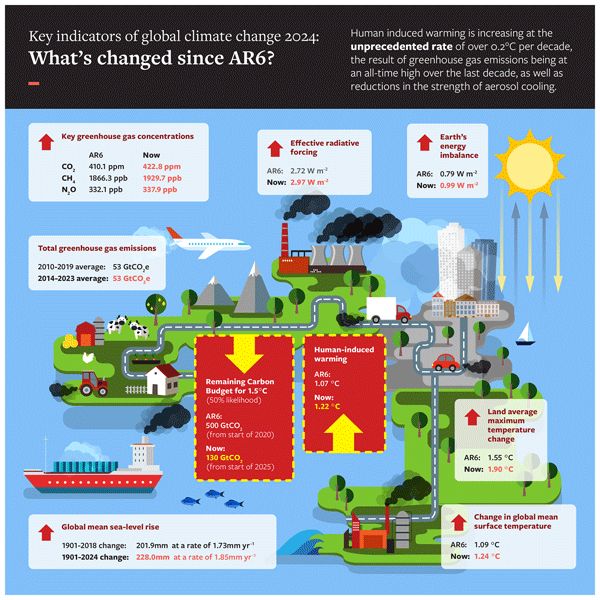
⬆️ Human induced warming now at 1.36C
⬆️ Rate of warming now 0.27C / decade
⬆️ Sharp increase in Earth's energy imbalance
⬇️ Remaining 1.5C carbon budget only 130 GtCO2
essd.copernicus.org/...
Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
🎵Amazing and inspiring work - check it out!


Reposted by: Frank Pattyn, Jean P. v. Ypersele
Le tout est à lire ici, via @lechobe.bsky.social 👇
www.lecho.be/economie-pol...

Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
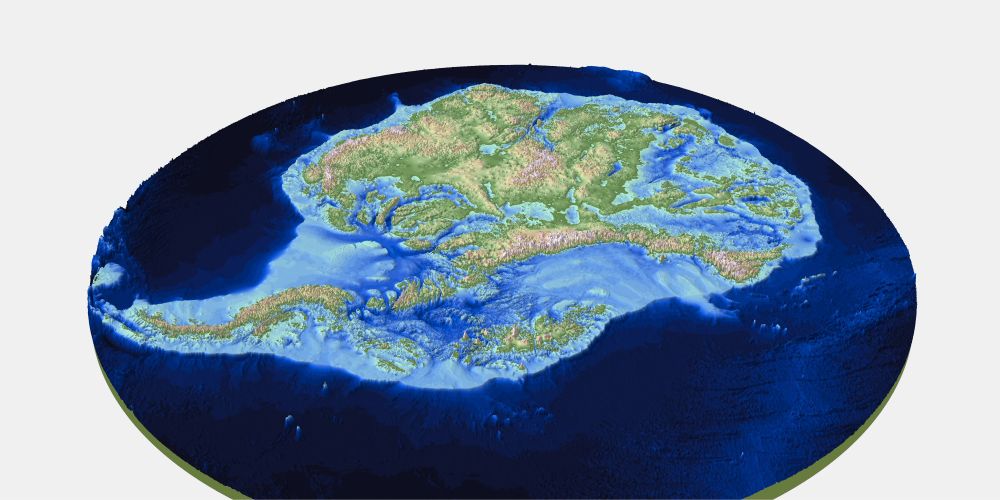
Graphic: Hamish Pritchard et al
Reposted by: Frank Pattyn

Reposted by: Frank Pattyn

Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
view.genially.com/677e7c942787...
by Xavier Fettweis — Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
www.rtbf.be/article/le-p...

Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
Submersion, created by @h2020protect.bsky.social and featuring art and science, delves into the impact of melting glaciers and rising seas
🗓️Feb 1–Mar 1, 2025
📍Saint-Martin d'Hères, France
🔗 Learn more: protect-slr.eu/2025/01/15/s...


Reposted by: Frank Pattyn
👉Even low emissions could lock in meters of #SeaLevelRise from Antarctica, while high emissions could trigger up to +40m over millennia
👉We must consider long-term sea-level commitment in coastal planning
🔗 protect-slr.eu/2025/01/15/n...

Reposted by: Frank Pattyn