Lab website: https://www.demendozalab.com/
1) active histone mods occur independently of transcription
2) transcription coordinates histone deacetylation at active promoters
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

1) active histone mods occur independently of transcription
2) transcription coordinates histone deacetylation at active promoters
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...


Writing this with Olga @orpsf.bsky.social & Didier @trono-lab.bsky.social was a major highlight of my 🇨🇭sabbatical. Such a treat! 🍫Hope you enjoy it as much as we enjoy piecing it together.

Writing this with Olga @orpsf.bsky.social & Didier @trono-lab.bsky.social was a major highlight of my 🇨🇭sabbatical. Such a treat! 🍫Hope you enjoy it as much as we enjoy piecing it together.
Donal O’Carroll and coworkers
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

Donal O’Carroll and coworkers
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

📅 Starting date early 2026, with some flexibility.
🙏Please, RT!

📅 Starting date early 2026, with some flexibility.
🙏Please, RT!
A lot of debugging & highlights how even simple components in synthetic biology can have unexpected properties.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

A lot of debugging & highlights how even simple components in synthetic biology can have unexpected properties.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
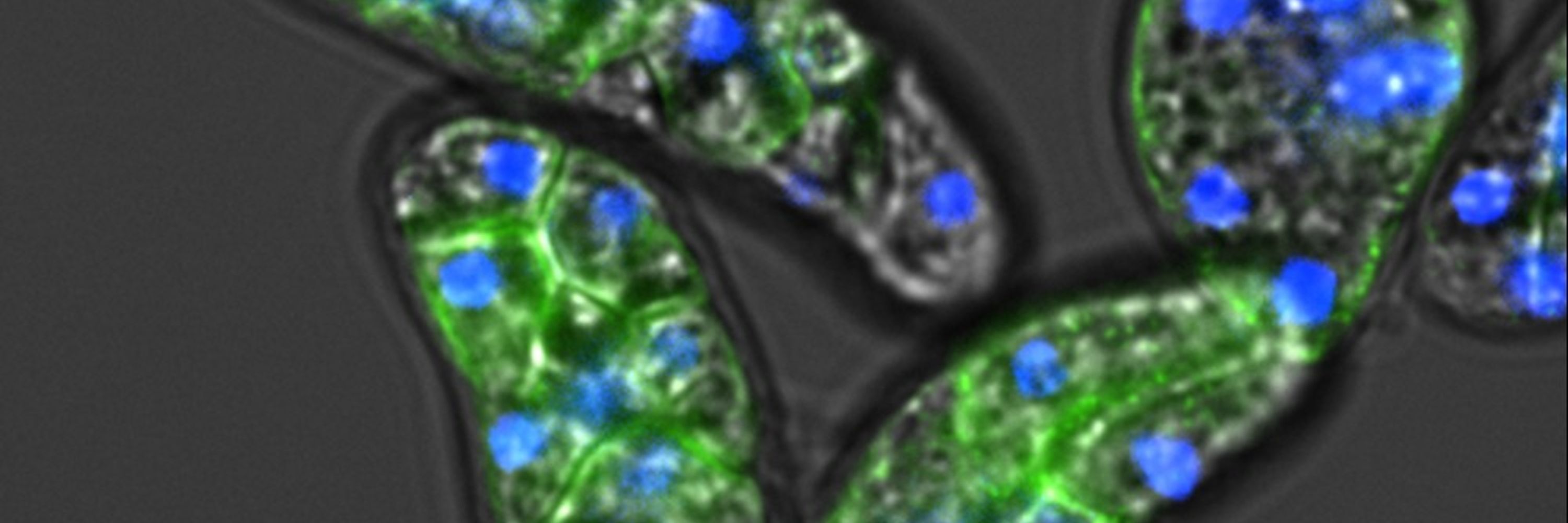
We show that #Expansion #Microscopy is a broad-spectrum modality for Euks, enabling 3D phenotypic maps rooted to phylogeny.
#ProtistsOnSky #SciComm #SciSky
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
We show that #Expansion #Microscopy is a broad-spectrum modality for Euks, enabling 3D phenotypic maps rooted to phylogeny.
#ProtistsOnSky #SciComm #SciSky
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...


www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
rdcu.be/eLbaZ

rdcu.be/eLbaZ
How does genetic architecture constrain evolutionary trajectories? To address this question, we inferred the genetic architecture of convergent plumage coloration and its evolutionary history in wheatears.

#RNAbiology #TEsky #smallRNAs #PRC2 #DNAelimination
1/5
academic.oup.com/nar/article-...

#RNAbiology #TEsky #smallRNAs #PRC2 #DNAelimination
1/5
academic.oup.com/nar/article-...
This is two stories in one: a case study/cautionary tale on developing genetic tools in new organisms, and the first hint at a gene regulatory network for choanoflagellate multicellular development (which turn out to involve a Hippo/YAP/ECM loop!) A 🧵

This is two stories in one: a case study/cautionary tale on developing genetic tools in new organisms, and the first hint at a gene regulatory network for choanoflagellate multicellular development (which turn out to involve a Hippo/YAP/ECM loop!) A 🧵







